
Skin diseases
REDUCTION OF INFLAMMATORY PROCESSES IN THE SKIN FOR PSORIASIS AND ALLERGIC DERMATITIS
A graphical representation of a study where the addition of antioxidants to the diet of mice demonstrated a significant reduction in the inflammatory process in the skin for conditions such as psoriasis and allergic dermatitis.
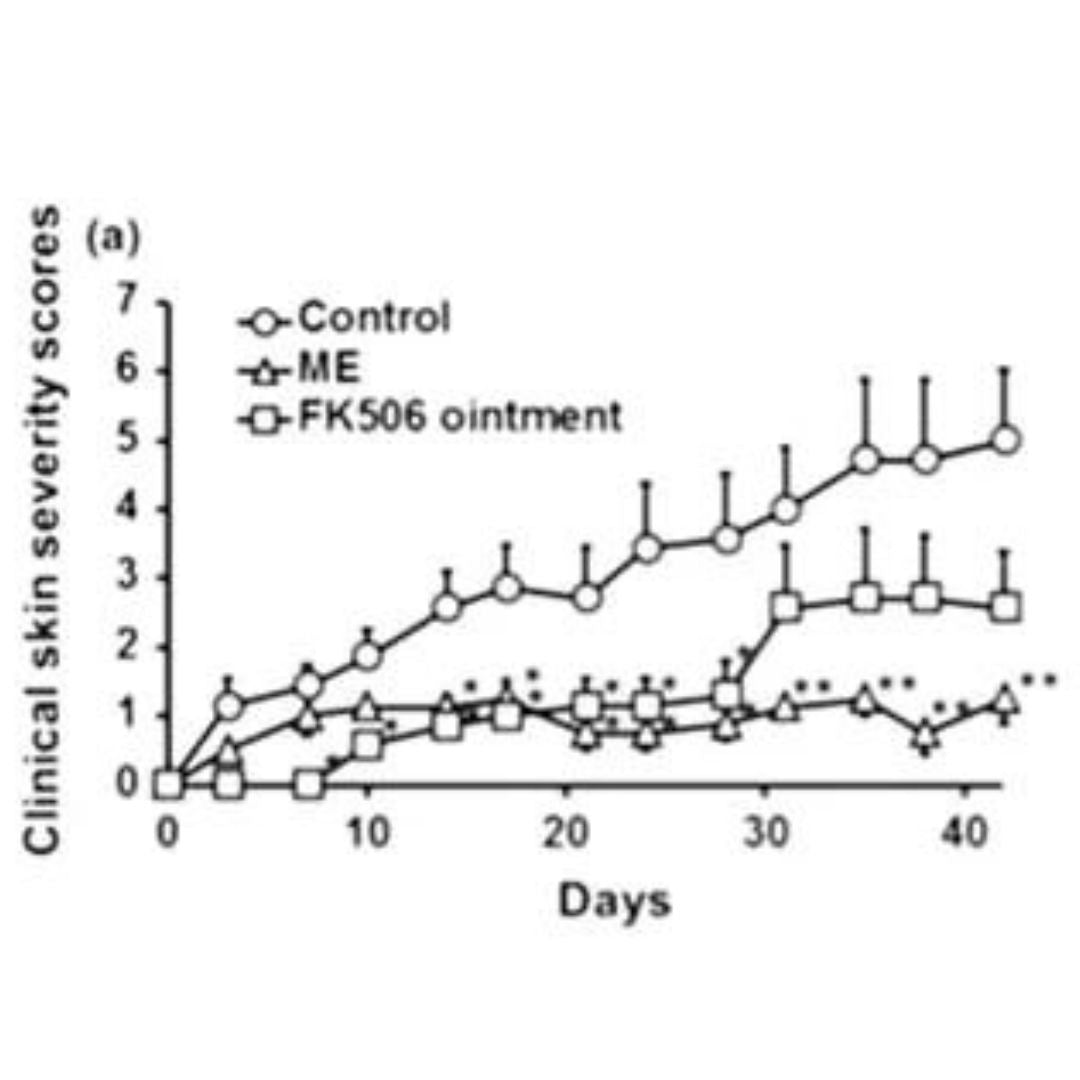
The graph shows the rate of formation of pathologically altered epidermal cells that lead to flaking in allergic dermatitis and the formation of scales in psoriasis. It shows the effect of antioxidants on significantly reducing inflammation and keratinization of the skin in allergic dermatitis and psoriasis.
Circle:
The upper curve shows what happens in the skin when no treatment is given.
Square:The middle curve shows the effect of anti-inflammatory ointments used topically.
Triangle:The lower curve shows how the disease processes in the skin significantly slow down when antioxidants appear in the blood. Over time, the effect of antioxidants increases.
Graphs c and d show how the frequency of skin scratching every 20 minutes and the duration of scratching every 20 minutes due to skin itching significantly decreased after the use of antioxidants.
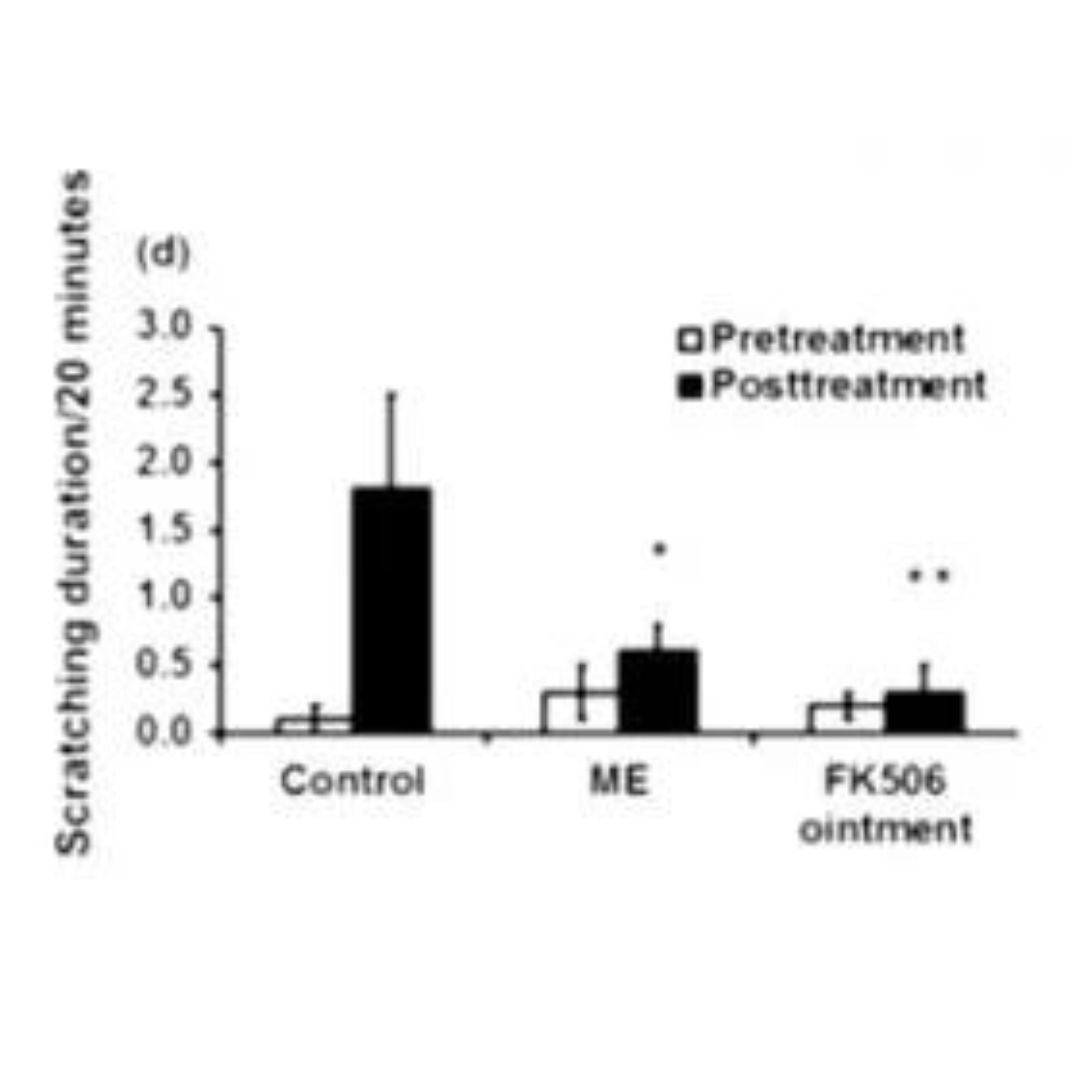
Therefore, it demonstrates that itching of the skin, which is besides the aesthetic changes the biggest problem of these chronic skin diseases, is significantly alleviated.
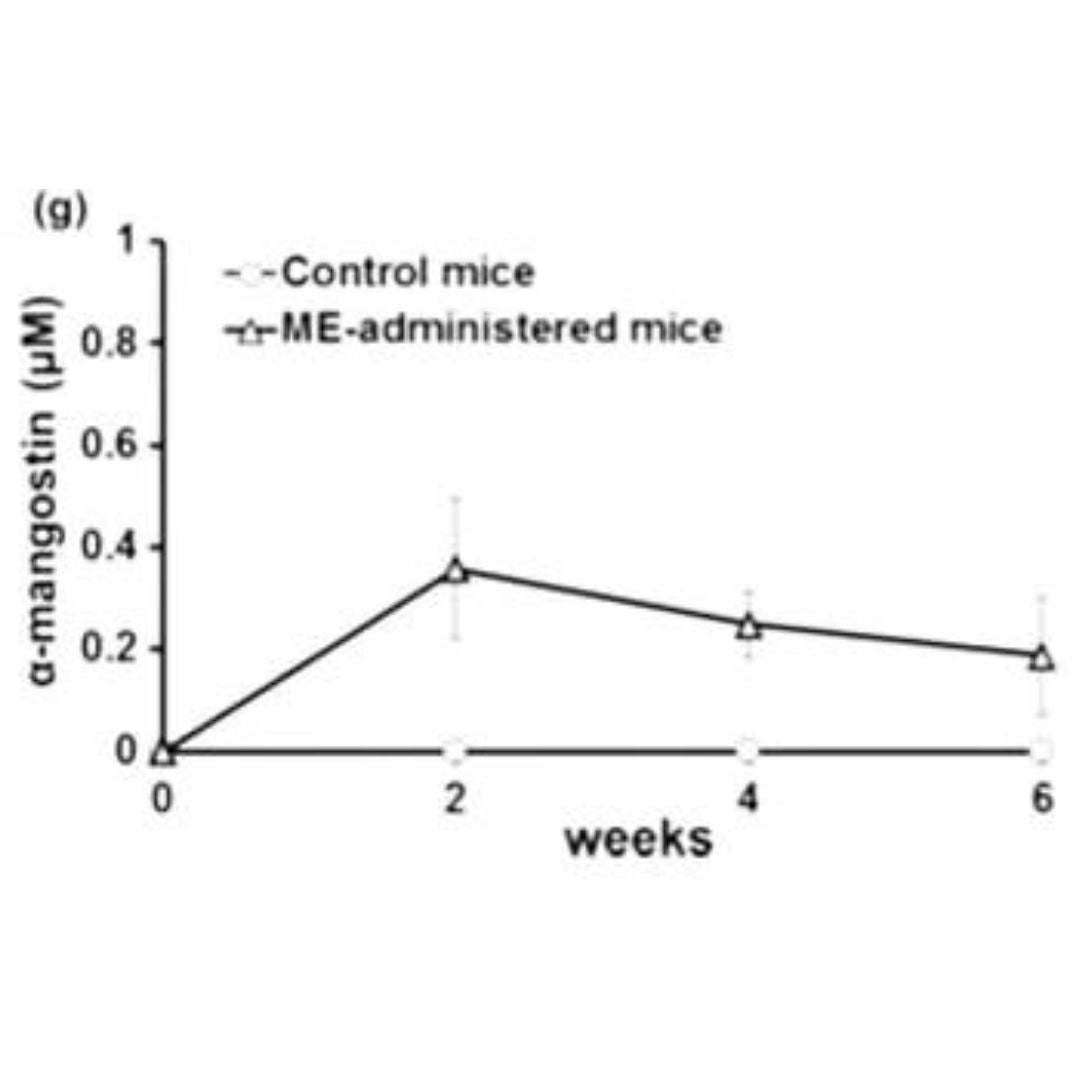
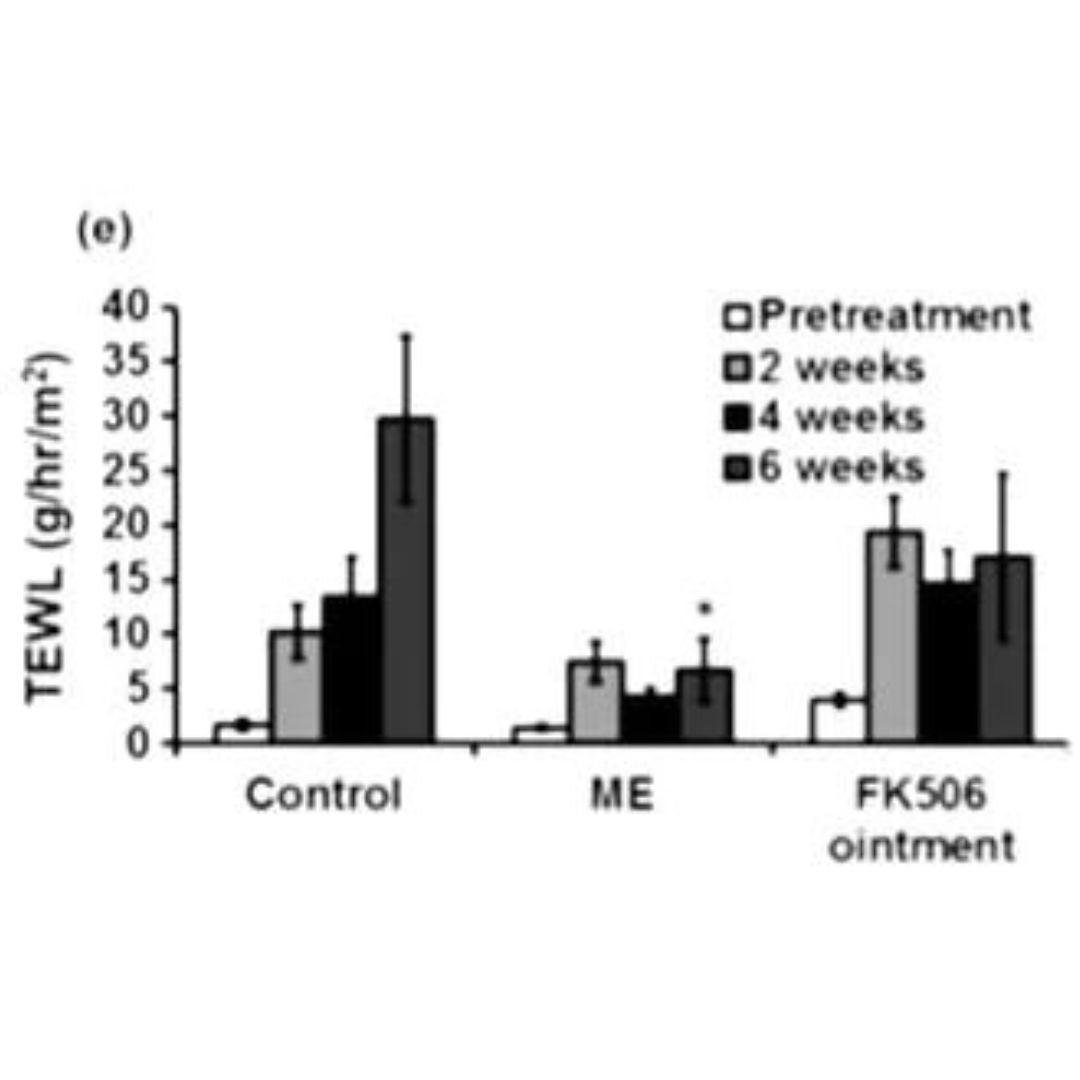
The graph shows the passage of fluid from inflamed skin cells, leading to the formation of skin swelling. When the inflammation subsides, the passage of water from the skin cells significantly decreases or stops.
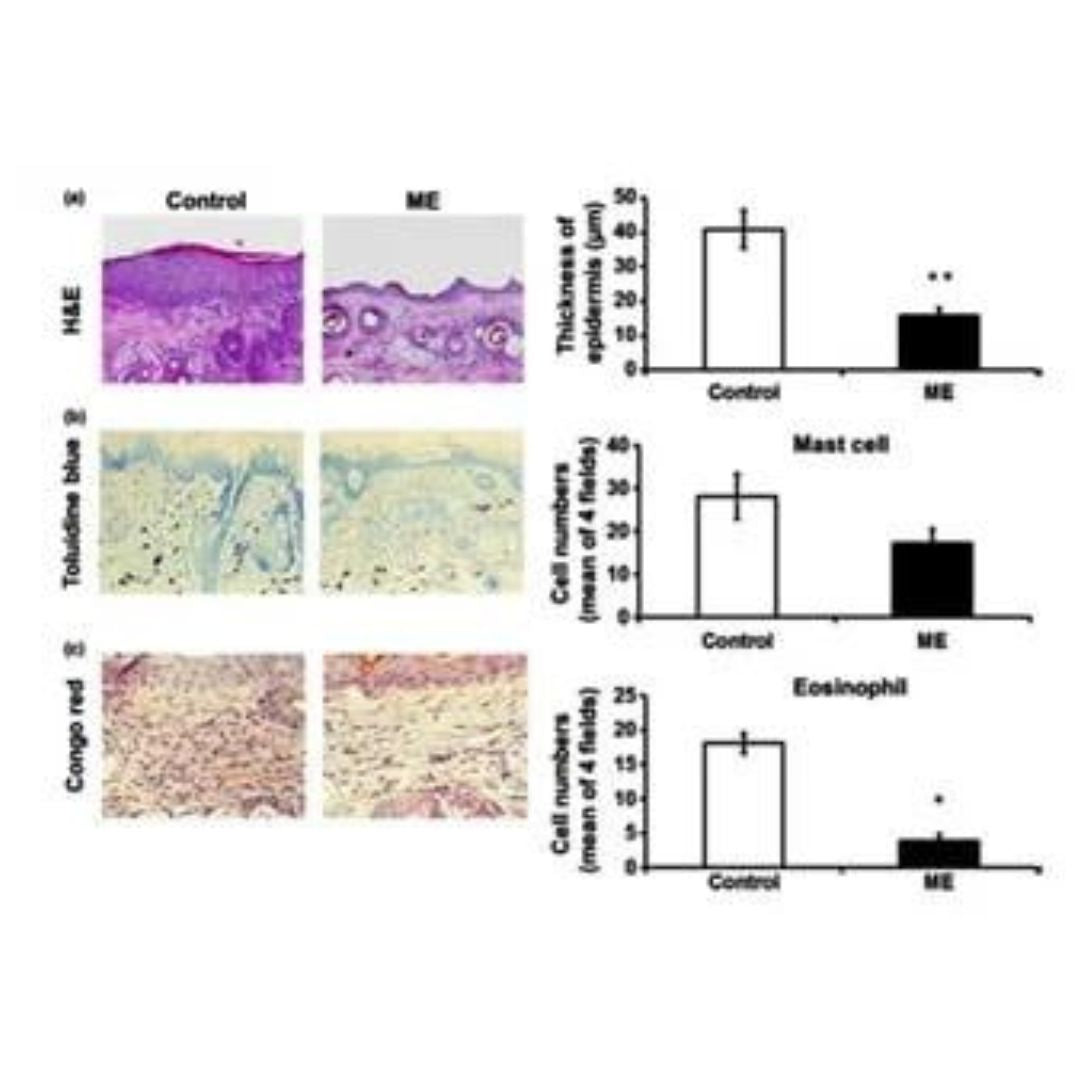
Pictures a, b, and c show a histological view (examination of the skin under a microscope), how antioxidants significantly reduce the number of inflammatory cells in the skin in allergic dermatitis and psoriasis.
On the left are skin preparations of a mouse that did not consume antioxidants and on the right in the skin of a mouse that regularly consumed antioxidants. The small darker stained cells (different dyes for different inflammatory cells) are inflammatory cells, which visibly decrease in the skin after consuming antioxidants.
The reduction of inflammatory cells means the calming of disease signs of psoriasis and allergic dermatitis.
Viri: J Dermatol. 2013 Oct;40(10):786-96. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12250. Epub 2013 Aug 21. Suppressive effect of mangosteen rind extract on the spontaneous development of atopic dermatitis in NC/Tnd mice. Higuchi H1, Tanaka A, Nishikawa S, Oida K, Matsuda A, Jung K, Amagai Y, Matsuda H. Recent advances in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis: genetic background, barrier function, and therapeutic targets. Miyagaki T1, Sugaya M2.